- Home
- About us
- Products
- Disposable Wooden Cutlery Wholesale
- Ice Cream Sticks and Spoons Wholesale
- Coffee Stirrers Wholesale
- Skewers Wholesale
- Disposable Chopsticks Wholesale
- Toothpicks Wholesale
- Disposable Wooden Food Containers Wholesale
- Eco-friendly Straws Wholesale
- Disposable Wooden Medical Supplies Wholesale
- Disposable Wooden Beauty Salon Supplies Wholesale
- Faqs
- News
- Certificate
- Contact us
-
-

-
Current Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) for Human Food
Certificate No : NSF25GMP03002
Issuing authority : NSF Shanghai Co., Ltd.
Valid period : 2025/4/12 - 2026/4/11
What is GMP?
Good Manufacturing Practices, or GMP, represent a set of stringent and meticulously designed standards that govern the production processes in various industries to ensure the quality, safety, and consistency of the final products. These practices are particularly crucial in sectors such as food, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and medical devices, where product integrity is vital for consumer safety and efficacy.GMP provide a framework that outlines the necessary conditions and parameters an operation must maintain to produce high-quality products reliably. The system covers everything from raw material procurement to final product delivery, ensuring each step meets specific quality criteria.The quality management aspect of GMP focuses on establishing a culture of continual improvement within the manufacturing facility. It ensures that all employees understand their role in maintaining product quality and adhere to standard operating procedures (SOPs). This includes training programs, procedure manuals, and regular review of processes to identify areas for enhancement.Sanitation and hygiene are critical in preventing product contamination and cross-contamination. GMP guidelines require rigorous cleaning and disinfection protocols for equipment, tools, and the production environment. Personal hygiene among personnel is also emphasized, including the use of proper attire, handwashing stations, and restrictions on eating and drinking in production areas.Facilities and building requirements under GMP are designed to promote a clean, well-organized, and appropriately zoned working space. Manufacturing areas must be maintained at certain temperature and humidity levels, with airflow systems that minimize contamination risk. Equipment placement and workflow design should preventmix-ups and facilitate one-way traffic to avoid cross-contamination.Equipment used in the manufacturing process must be designed for ease of cleaning and maintenance. Regular calibration and inspection of machinery are required to ensure it operates correctly and consistently, thus maintaining product quality. Equipment should be appropriate for its intended use, with smooth surfaces to prevent accumulation of debris and a design that allows for thorough cleaning.Raw materials must meet strict specifications regarding identity, strength, quality, and composition. They should be stored properly to prevent degradation and must be traceable for lot accuracy. This ensures that any potentialquality issue can be quickly identified and contained, protecting both the consumer and the manufacturer’s reputation.Personnel play a crucial role in GMP compliance. All staff must receive extensive training on GMP requirementsand their responsibilities within the system. There must be clear policies on work attire, personal hygiene, and behavior in production areas to prevent human error or contamination that could compromise product quality.Validation and qualification activities confirm that processes, procedures, and equipment operate correctly and consistently deliver the desired results. Process validation involves detailed documentation of all critical steps in the manufacturing process, ensuring each can reliably produce quality products. Equipment qualification ensures machines perform accurately and consistently over time.Effective complaint handling is integral to GMP, providing a mechanism for addressing customer issues and concerns. Complaints are thoroughly investigated and resolved, with appropriate corrective actions taken to addressany underlying quality issues.Documentation and record-keeping are vital for demonstrating GMP compliance and facilitating regulatory audits. All aspects of the manufacturing process, from equipment maintenance to production batches, must be meticulously documented. Records must include accurate details of production runs, quality control checks, and any deviations or corrective actions taken.Regular inspections and quality audits help maintain continuous compliance with GMP standards. Internal and external audits assess the effectiveness of the quality system, identifying areas for improvement and verifying that established procedures are followed consistently.In summary, GMP are essential for ensuring that manufactured products are safe, effective, and of high quality. They provide a comprehensive blueprint for every step in the manufacturing process, from raw materials to finished goods, creating a culture of quality throughout the organization. Through meticulous planning, rigorous execution, and continual improvement, GMP serve as the backbone of quality assurance in manufacturing environments worldwide.
Good Manufacturing Practices or GMP is a system that consists of processes, procedures and documentation that ensures manufacturing products, such as food, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical goods, are consistently produced and controlled according to set quality standards. Implementing GMP can help cut down on losses and waste, avoid recall, seizure, fines and jail time. Overall, it protects both company and consumer from negative food safety events.GMP examine and cover every aspect of the manufacturing process to guard against any risks that can be catastrophic for products, such as cross-contamination, adulteration, and mislabeling. Some areas that can influence the safety and quality of products that GMP guideline and regulation address are the following:● Quality management● Sanitation and hygiene● Building and facilities● Equipment● Raw materials● Personnel● Validation and qualification● Complaints● Documentation and record keeping● Inspections and quality auditsIf you need to view the original document of our certificate, please contact us to obtain the download permission password.

-
-
-

-
BRC British Retail Consortium
Certificate No : C0749476-BRC3
Issuing authority : NSF Certification, LLC
Valid period : 2025/3/4 - 2026/5/10
What is BRC?
The BRC Global Standard is a widely recognized and respected certification in the food industry, setting the benchmark for quality and safety in food production. As an integral part of the Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI), BRC's standard harmonizes food safety systems across different regions and countries, ensuring that food manufacturers and their suppliers consistently meet high standards of safety and quality.The BRC standard encompasses comprehensive requirements tailored to various segments within the food industry, including Food Safety, Packaging and Packaging Materials, Storage and Distribution, Agents and Brokers, and Consumer Products. Each of these categories is subject to stringent criteria aimed at safeguarding the interests of the end consumer by ensuring that every link in the supply chain operates at the highest level of safety and quality.One of the key objectives of the BRC Global Standard is to protect the consumer by minimizing any potential risks associated with food production and supply. By implementing a set of uniform standards, BRC ensures that all certified organizations adhere to best practices in food safety management, thus reducing the likelihood of food-borne illnesses and other health concerns.To achieve this goal, the BRC Global Standard outlines a series of requirements that food processors must follow to build an effective food safety management system. These requirements span across various aspects of the food production process, from raw material procurement and handling to product development, manufacturing, packaging, storage, and distribution.In addition to outlining specific operational procedures, the BRC Global Standard also emphasizes the importance of a robust quality management system. This includes having well-documented processes, regular training programs for employees, and a culture of continuous improvement within the organization. By fostering such a culture, BRC aims to create an environment where quality and safety are prioritized at every level of the organization.Packaging and Packaging Materials form another crucial component of the BRC Global Standard. Proper packaging is essential to maintain the integrity and safety of food products during transportation and storage. The standard specifies requirements for packaging materials to ensure they do not introduce contaminants or negatively impact food safety. It also addresses labeling issues to guarantee that consumers receive accurate and clear information about the product.Storage and Distribution are equally critical in maintaining the safety and quality of food products. The BRC Global Standard sets forth guidelines for the proper storage conditions to prevent spoilage and contamination. It also covers logistics and distribution processes, ensuring that products are handled and transported in a way that preserves their integrity until they reach the end consumer.Agents and Brokers, who play a significant role in the food supply chain, are not left out in the BRC Global Standard. The standard mandates that these intermediaries understand and apply food safety principles in their operations to avoid compromising the safety and quality of the products they handle.Lastly, Consumer Products fall under the ambit of the BRC Global Standard. This category includes non-food items that come into contact with food, such as cleaning chemicals and personal care products. The standard ensures that these products are manufactured and handled in a way that does not pose risks to the safety of the food they may come into contact with.Overall, the BRC Global Standard provides a comprehensive framework for food safety and quality management. By adhering to these standards, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to protecting consumers and meeting their legal obligations. Certification to the BRC Global Standard not only enhances a company's reputation but also provides a competitive edge in the global marketplace. Through its rigorous criteria and focus on continuous improvement, the BRC Global Standard plays a vital role in promoting safety and quality within the global food industry.If you need to view the original document of our certificate, please contact us to obtain the download permission password.

-
-
-

-
ISO 9001:2015
Issuing authority : Bureau Veritas Certification Holding SAS – UK
Valid period : 2018/4/24 - 2027/4/23
What is ISO 9001:2015?
ISO 9001 is an international quality management system (QMS) standard intended to assist organizations in ensuring the consistent provision of products and services that meet customer and regulatory requirements, while achieving continuous improvement and enhancing customer satisfaction.Core Features of ISO 9001:1. Universality: The ISO 9001 standard is applicable to organizations of all types and sizes, whether they are in manufacturing, service industries, or non-profit organizations.2. Quality Management Principles: The standard is grounded on seven quality management principles, including customer focus, leadership, involvement of people, process approach, improvement, factual approach to decision making, and relationship management.3. Process Approach: The standard encourages organizations to use a process approach to manage activities more efficiently.4. Continuous Improvement: ISO 9001 emphasizes the continuous improvement of the QMS through internal audits, monitoring mechanisms, and process evaluations.5. Customer Satisfaction: An organization's quality management system should focus on meeting customer requirements and expectations to increase satisfaction.6. Top Management Commitment: Senior management must demonstrate commitment to the QMS through policy development, goal setting, and resource allocation to support quality objectives.7. Employee Training and Involvement: ISO 9001 stresses the importance of adequate training and motivation for employees to ensure their full involvement and contribution to quality management.8. Monitoring and Measurement: Organizations need to monitor and measure the performance of their QMS and make management decisions based on data and analysis.9. Risk Management: The standard requires organizations to identify, evaluate, and address risks and opportunities.Structure of the ISO 9001 Standard:The ISO 9001 standard is structured into several sections, each corresponding to different requirements, including:- Scope: Defines the applicability of the standard and the requirements organizations must follow.- Normative References: Lists the regulations and standards that must be referenced when implementing the standard.- Terms and Definitions: Provides professional terminology and definitions related to the QMS.- Quality Management System: Details the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving the QMS.Achieving ISO 9001 certification indicates that an organization has established a quality management system that meets these requirements, which not only boosts customer trust but also helps improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance product and service quality. Through continuous monitoring and improvement, organizations can optimize their quality management practices to adapt to market changes and evolving customer need.If you need to view the original document of our certificate, please contact us to obtain the download permission password.

-
-
-

-
LFGB for wooden items
Issuing authority : SGS
Valid period : 2022/1/14 - 2027/1/13
What is LFGB for wooden items?
The LFGB certificate is a prestigious endorsement that attests to the compliance of food contact materials with stringent German and European safety standards. This certification is highly regarded by manufacturers and consumers alike, as it serves as a guarantee that products undergoing this rigorous testing meet the highest criteria for safety and quality. The LFGB testing encompasses various aspects, including sensory evaluation, chemical migration, and verification of label claims, ensuring that materials coming into contact with food are free from harmful substances and safe for consumption.One of the crucial tests included in the LFGB certification process pertains to the specific migration of formaldehyde (§30 LFGB Regulation (EC) 1935/2004). Formaldehyde is a well-known substance with potential health risks, and its presence in food contact materials is strictly regulated. The LFGB certification ensures that the migration levels of formaldehyde from the product to food simulants remain within the safety limits established by the regulation. This scrutiny is vital in safeguarding consumer health and preventing any adverse effects that might arise from exposure to excessive levels of formaldehyde.Another essential test conducted under the LFGB certificate is the sensory test (§31 LFGB Regulation (EC) 1935/2004). This evaluation involves a panel of trained sensory assessors who meticulously examine the product for any off-odors or tastes that might be imparted to food. The sensory test is critical because it directly impacts the organoleptic properties of the food that comes into contact with the material. By ensuring that the product does not transfer any detrimental odors or tastes to food, the LFGB certification helps maintain the integrity and palatability of the food items, thereby preserving their quality and appeal.Furthermore, the LFGB certification also addresses the content of Pentachlorophenol (PCP), a substance that has been banned in many countries due to its toxicity and environmental persistence. The LFGB testing procedure checks for the presence of PCP in food contact materials, ensuring that they are completely free from this hazardous compound. This measure is significant in protecting both human health and the environment from the potential dangers associated with PCP exposure.In addition to these tests, the LFGB certification also verifies the validity of label claims, such as Bisphenol-A (BPA) free products. This verification process involves determining the total content of Bisphenol A in the product to confirm that it indeed does not contain this controversial substance. Bisphenol A has raised concerns over potential health risks, particularly related to hormone disruption. By certifying products as BPA-free through comprehensive testing, the LFGB endorsement provides consumers with peace of mind, knowing that their chosen products uphold this claim and are safe for use in contact with food.The LFGB certificate, therefore, stands as a hallmark of excellence and safety in the realm of food contact materials. Its comprehensive testing protocols go above and beyond basic regulatory requirements, ensuring that certified products not only comply with the law but also embody the highest standards of quality and safety. Manufacturers who bear the LFGB certification can pride themselves on their commitment to consumer welfare and environmental protection, while consumers can trust that their choices are backed by one of the most stringent and reputable certifications available. In an era where safety and transparency are paramount, the LFGB certificate shines as a beacon of trustworthiness and responsibility.
Most of our products have passed the test under §30 and §31 LFGB Regulation (EC) 1935/2004A. Sensory testB. Specific migration of formaldehydeC. Pentachlorophenol (PCP) ContentD. Verification for label claim validity- Bisphenol-A free by Total Content of Bisphenol AIf you need to view the original document of our certificate, please contact us to obtain the download permission password.

-
-
-

-
U.S FOOD&DRUG ADMINISTRATION (FDA)
Issuing authority : Intertek Testing Services Shenzhen Limited, Guangz
Valid period : 2017/12/15 - 2027/12/14
What is FDA?
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is a federal agency dedicated to protecting public health through the regulation of a wide array of products, including foods, drugs, cosmetics, and medical devices. One particular area of regulation pertains to wood preservatives, which are substances applied to wood products to protect them against decay, insects, and other pests. The FDA has specific regulations governing the use of certain chemicals in these wood preservatives to ensure that they are safe for human contact and do not pose health risks.One such chemical that has been closely regulated by the FDA is pentachlorophenol (PCP). PCP has been used extensively in the past as a wood preservative due to its effectiveness in preventing wood decay and insect infestation. However, concerns over its potential health effects, particularly its classification as a probable human carcinogen, have led the FDA to impose strict regulations on its use. These regulations are outlined in 21 CFR Part 178.3800, which specifically addresses the use of PCP in wood preservatives.Under this regulation, the FDA mandates that PCP can only be used in accordance with specific guidelines that minimize its risk to human health. This includes limitations on the types of wood products that can be treated with PCP, the maximum amounts of PCP that can be used, and the required safety measures during application and subsequent handling of the treated wood.For companies exporting wooden products from the United States, compliance with these FDA regulations is not just a legal requirement but a crucial step in maintaining the trust and confidence of foreign customers and governments. To demonstrate this compliance, foreign customers or governments often request a certificate from the FDA attesting to the regulatory or marketing status of the products in question. An FDA certificate serves as an official document that provides information about a product's adherence to regulatory standards, acting as a seal of approval indicating that the product is safe for its intended use.In response to these certification requests, our company has taken great care to ensure that all our wooden products meet the rigorous standards set forth by the FDA regarding the use of PCP in wood preservatives. We understand that the safety and quality of our products are paramount, not only for the well-being of our customers but also for the reputation of our business on the global stage.To guarantee this compliance, we have implemented comprehensive quality control procedures at every stage of our production process. From sourcing raw materials to the final treatment and packaging of our wood products, we adhere strictly to the guidelines set out in 21 CFR Part 178.3800. Our commitment to excellence has resulted in our wooden products passing the stringent tests of the FDA regulation on wood preservatives, specifically concerning the controlled use of PCP.By obtaining an FDA certificate for our wooden products, we provide our foreign customers and partners with irrefutable proof of our commitment to safety and quality. This documentation not only strengthens the trust between us and our international clients but also enables us to navigate the complexities of global trade with confidence and transparency.Furthermore, our dedication to meeting FDA standards reflects our broader company ethos of responsibility and sustainability. Recognizing the impact our actions have on both people and the environment, we strive to manufacture products that contribute to a healthier world for all. Our compliance with FDA regulations regarding PCP in wood preservatives is just one aspect of this commitment, demonstrating our resolve to uphold the highest possible standards in all that we do.In conclusion, the U.S. FDA plays a pivotal role in ensuring the safety of various products, including wood preserved with chemicals like PCP. Through regulations such as 21 CFR Part 178.3800, the FDA helps safeguard the health of consumers while also guiding businesses like ours towards responsible practices that benefit both people and the planet. By adhering to these regulations and obtaining FDA certificates for our wooden products, we affirm our dedication to safety, quality, and sustainability, building enduring relationships with our customers based on trust and mutual respect.If you need to view the original document of our certificate, please contact us to obtain the download permission password.

-
-
-

-
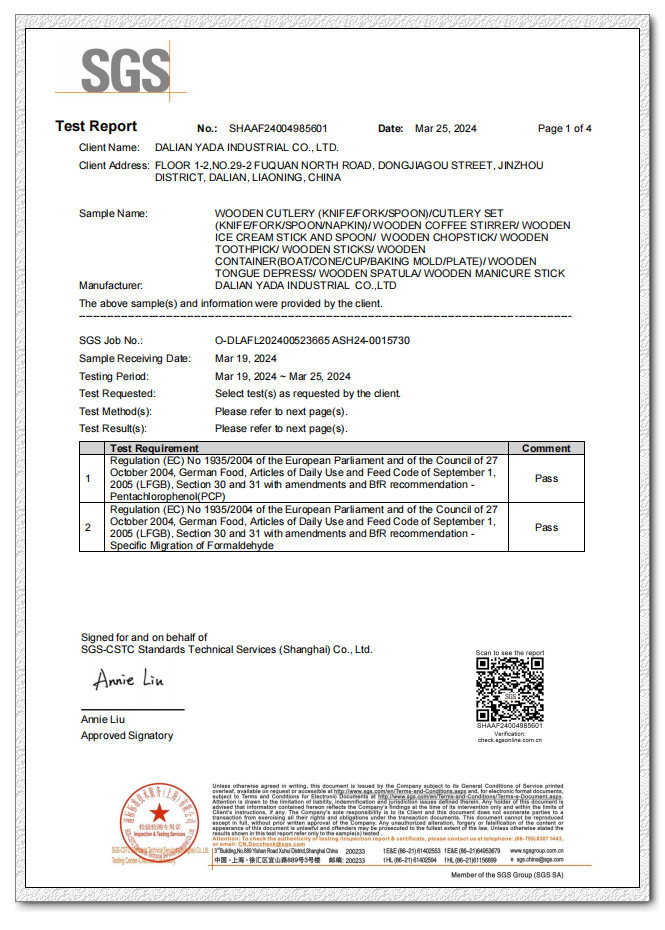
SGS
Issuing authority : SGS
Valid period : 2018/9/14 - 2028/9/13
SGS: Global Partner in Quality Assurance.
SGS: Your Global Partner in Quality AssuranceSGS, a global leader in inspection, verification, testing, and certification, offers core services to help clients meet quality standards and regulatory challenges across different regions and markets.SGS's inspection services are comprehensive, performing extensive inspections and verification that enable clients to maintain product quantity and quality, and ensure compliance across various markets. These services are based on deep industry knowledge and technical expertise, ensuring consistency and reliability of products and services globally.Equipped with advanced laboratory facilities, SGS is capable of precise testing on products ranging from raw materials to finished goods. This ensures all products comply with strict technical specifications and industry standards, regardless of where they will be sold or used. Such thorough testing not only enhances product quality but also strengthens consumer trust in the brand.In the realm of certification, SGS provides a variety of certification services that help clients prove their products or services meet international and local standards. These certifications serve as more than just marks of market entry; they symbolize efficient management and superior performance, helping businesses stand out in competitive markets.To support companies in achieving sustainability goals, SGS offers a range of sustainability services including aiding enterprises in obtaining certifications like ISO 14001 and OHSAS 18001. By guiding businesses through environmental and social responsibility requirements, SGS helps establish sustainable business models that improve operational efficiency while demonstrating corporate social responsibility.Additionally, SGS provides technical support, assisting businesses in anticipating and addressing potential quality issues during the product development phase. From product design consultation to post-market surveillance, SGS's expert team supports throughout the process, ensuring high-quality standards from concept to consumer.In terms of training services, SGS offers customized training programs designed to elevate employees' understanding of quality management systems and specialized skills needed in regulated industries. This training equips staff with the knowledge to understand industry best practices and apply them in their daily work, thereby enhancing overall business performance.For risk management, SGS presents comprehensive solutions that help businesses assess and mitigate risks such as supply chain risks, product safety hazards, and operational compliance issues. These services protect a company's brand reputation and reduce financial impacts.With its broad range of services and industry expertise, SGS ensures its clients can trade smoothly in the global market while adhering to all relevant laws and regulations. Collaborating with SGS enables businesses to ensure their processes, products, and services not only meet current needs but also anticipate and adapt to future challenges.If you need to view the original document of our certificate, please contact us to obtain the download permission password.
-
-
-

-
FSC
Certificate No : GFA-COC-007676
Issuing authority : GFA Certification GmbH
Organization phone : +49 40 5247431 0
Valid period : 2024/5/23 - 2029/5/22
What is FSC?
The Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) is an international non-profit organization that promotes responsible forestry and sustainable woodland management. By certifying products like wooden cutlery, stirrers, ice cream sticks, and spoons, the FSC ensures they are made from responsibly sourced wood, contributing to a smaller environmental footprint.The FSC's certification system is based on a set of stringent standards that cover all aspects of forest management, from conservation values and ecosystem diversity to social impacts on local communities. These standards are designed to ensure that forestry operations respect biodiversity, protect natural habitats, and maintain the health of forest ecosystems for future generations.One of the key principles of FSC certification is the concept of "multifunctional" forest management, which recognizes that forests provide not only wood but also other ecological services such as carbon storage, water regulation, and habitat for wildlife. By adhering to these principles, FSC-certified forests contribute to a more holistic approach to land use, balancing economic activity with ecological integrity.When a product bears the FSC logo, consumers can be confident that it has met rigorous environmental and social criteria. This includes requirements for traceability throughout the supply chain, from the forest where the trees are grown to the final product manufactured. It also means that the timber used in these products comes from forests that are managed in a way that:- Avoids conversion of forests to other uses, such as agriculture or urban development.- Ensures the rights of local people and indigenous communities are respected.- Promotes beneficial relationships between forest managers and local communities.- Protects rare, threatened, or endangered species and their habitats.- Maintains or enhances the forest's ecology and biodiversity.The FSC's commitment to environmental responsibility extends beyond the forest itself. It also takes into account the entire lifecycle of the product, including its manufacture and eventual disposal. For example, FSC certified wooden cutlery should be produced in facilities that minimize waste and pollution, using sustainable energy sources where possible. The processing of the wood should also avoid the use of harmful chemicals, ensuring that the final product is safe for both consumers and the environment.Furthermore, FSC certification encourages the use of materials from well-managed forests over non-renewable alternatives like plastic. Wooden cutlery and other utensils made from FSC-certified wood offer a sustainable choice for consumers who want to reduce their plastic consumption and support responsible forestry practices.In terms of social responsibility, the FSC's standards require companies to ensure fair working conditions, prohibit discrimination and child labor, and promote safe and healthy workplaces. This means that the production of FSC certified wooden products upholds social as well as environmental standards, contributing to a more equitable global economy.In conclusion, the Forest Stewardship Council plays a crucial role in promoting sustainable forestry and responsible sourcing of wood products. By choosing FSC certified wooden cutlery, stirrers, ice cream sticks, and spoons, consumers can be part of a larger movement towards preserving forests and ensuring they are managed in a way that benefits both people and the planet. With strict standards that cover everything from ecosystem health to social equity, FSC certification is a powerful tool for positive change in the world of forestry and beyond.If you need to view the original document of our certificate, please contact us to obtain the download permission password.

-
-
-

-
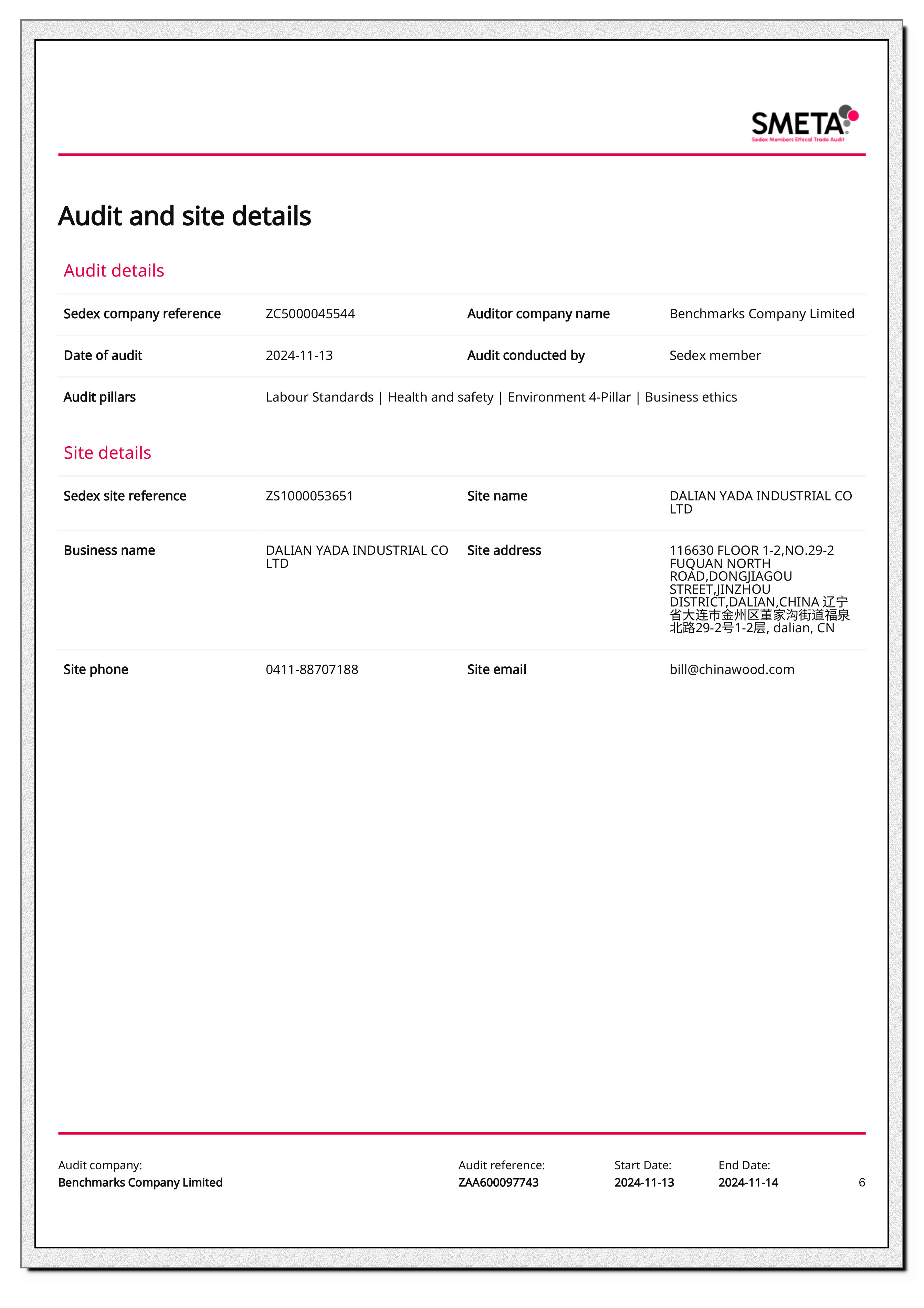
Sedex
Certificate No : ZS1000053651
Issuing authority : Benchmarks Company Limited
Valid period : 2024/11/13 - 2025/11/14
YADA's Certification - Sedex
As a company committed to sustainable development and social responsibility, YADA understands the importance of supply chain management in a globalized business environment. Therefore, we chose to partner with Sedex to enhance our business operations and brand image through its leading business ethics audit platform.Being certified by Sedex not only makes YADA stand out from the crowd, but also strengthens consumers' trust in our brand. This certification signifies our adherence to internationally recognized standards of social responsibility and demonstrates our commitment to sustainable development. At the same time, Sedex's SMETA audit results are accepted by a number of well-known brands and retailers around the world, meaning that one of our audits may be recognized by multiple customers, significantly saving the cost and time of repeated audits.Through regular Sedex audits, YADA ensures ongoing compliance with local laws and regulations as well as international standards of business ethics, which not only reduces the risk of legal action, but also enhances our compliance. In addition, Sedex has provided us with a systematic approach to assessing and managing ethical risks in our supply chain, helping us to build a more responsible and sustainable supply chain.Implementing Sedex standards has enabled us to provide a safer and healthier working environment for our employees, which has undoubtedly increased job satisfaction and loyalty. For YADA, which is looking to expand into international markets, Sedex certification is a gateway to certain international markets, particularly in Europe and North America, and it has helped us to expand our international business.The data sharing capabilities of the Sedex platform allow us to transparently demonstrate our social responsibility performance, which enhances the trust of our customers, investors and other stakeholders. Most importantly, Sedex not only focuses on our current compliance, but also encourages us to continuously improve our management
If you need to view the original document of our certificate, please contact us to obtain the download permission password.
-
-
-

-
SGS Test Report - Wooden Ice Cream Sticks for Microbial
Issuing authority : SGS-CSTC Standards Technical Services Co., Ltd.
Valid period : 2024/11/6 - 2025/11/6
SGS Test Report - Wooden Ice Cream Sticks for Microbial
This year's test report of ice-cream sticks adds some microbiological and sensory testing items on the basis of the national standard GB 4806.12-2022 National Standard for Food Safety Bamboo and Wooden Materials and Products for Food Contact. It follows the Q/DYXS 001-2024 Ice-cream Stick Enterprise Standard for testing. The enterprise standard is stricter than the national standard, and this change reflects that we attach great importance to the safety of our products and are responsible for the health of consumers.Total Bacteria: mainly to determine the degree of contamination of the product to ensure that the product leaves the factory in compliance with the standard requirements.Staphylococcus aureus: a common pathogenic bacteria, widely found in nature, such as soil, water, air, as well as the skin and nasal cavity of animals and humans. By detecting the presence of Staphylococcus aureus and its toxins in products, food poisoning incidents can be effectively prevented and food safety can be guaranteed.Common Physical and Chemical IndicatorsBamboo and wood products in the process of food contact, its surface coatings, adhesives, etc. may contain harmful substances, these substances may migrate to the food under specific conditions, which in turn have an adverse effect on human health, testing this item to ensure that it will not cause contamination of food in the process of use, thereby protecting the health and safety of consumers.Migrant indicators: (formaldehyde, sulfur dioxide, pentachlorophenol and its salts in terms of pentachlorophenol) are in line with the national standards in the limited indicator values.Residue indicators: (thiram, o-phenylphenol, myclobutanil, biphenyl) are in line with the national standards in the limited indicator values.Through such a comprehensive and detailed testing process, we hope to provide consumers with safer and more reliable products, and at the same time set a higher quality benchmark for the industry. In the future, we will continue to dedicate ourselves to technological innovation and service optimization, and strive to meet the growing demands of the market.If you need to view the original document of our certificate, please contact us to obtain the download permission password.

-
-
-

-
SGS Test Report - Wooden Ice Cream Sticks for Sensory, Defects of Material Quality, Moisture Content, Dimensional tolerance, Defects of Machining
Issuing authority : SGS-CSTC Standards Technical Services Co., Ltd.
Valid period : 2024/11/11 - 2025/11/11
SGS Test Report - Wooden Ice Cream Sticks for Sensory, Defects of Material Quality, Moisture Content, Dimensional tolerance, Defects of Machining
For this year's Ice Cream Stick test report, we have also added index tests for sensory requirements, material defects, water content, dimensional tolerances, processing defects, etc. based on corporate standards. The products are categorized into A, B and C grades according to various aspects such as quality, performance, appearance and price so that consumers can choose the right products according to their needs.1. Sensory requirementsWe have conducted detailed sensory evaluation of each batch of ice cream bars produced, including but not limited to:Whether the surface is clean and free from pollution;Whether the texture is smooth;Whether the odor is inherent to bamboo and wood No peculiar odor;Whether the package is intact and without damage.2. Material defectsMaterial defects are checked according to the original state of bamboo wood, including but not limited to:Whether the overall color is consistent;Whether there are insect holes, tree knots and decay;Whether there are black mineral lines and fluting on the surface;3. Dimensional specification inspectionIn order to ensure that every customer can have a satisfactory experience, all products before leaving the factory must undergo strict dimensional measurements to ensure that the length, width, thickness and other parameters of each ice-cream stick are in line with the design standards.4. Processing Defect InspectionThe products will be interfered by external substances during the production process, resulting in surface defects. We have refined the types of processing defects, and each batch of products leaving the factory is inspected in accordance with this type of defects, so that customers can better understand the quality and performance of the products.5. Other important indicatorsMoisture content: too high moisture content will lead to deformation, cracking and even rotting of wood, while too low moisture content will increase the hardness of bamboo wood and make it easy to break, so we test the products according to the batch to ensure the performance of the products and the quality of the finished products.Through this comprehensive and detailed testing process, we hope to provide consumers with safer and more reliable products, and at the same time set a higher quality benchmark for the industry. In the future, we will continue to devote ourselves to technological innovation and service optimization, and strive to meet the growing needs of the market.If you need to view the original document of our certificate, please contact us to obtain the download permission password.

-
